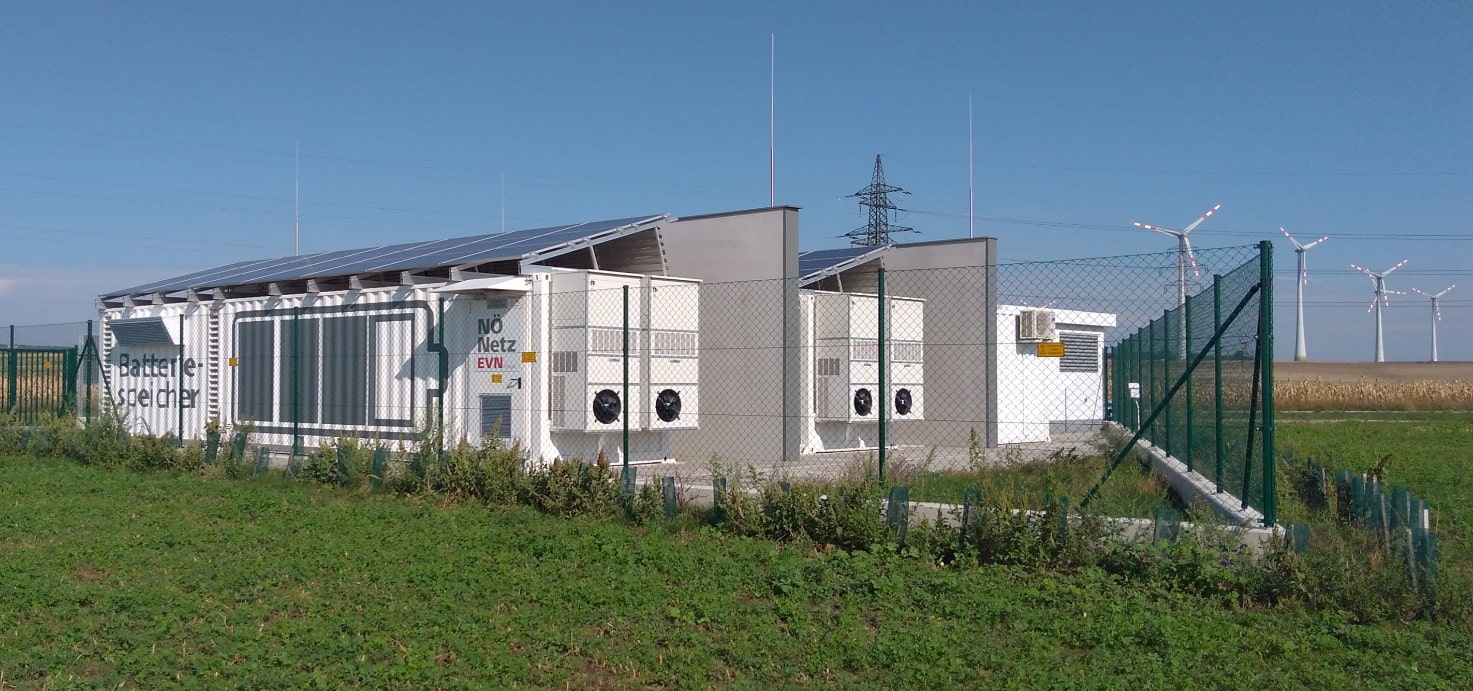
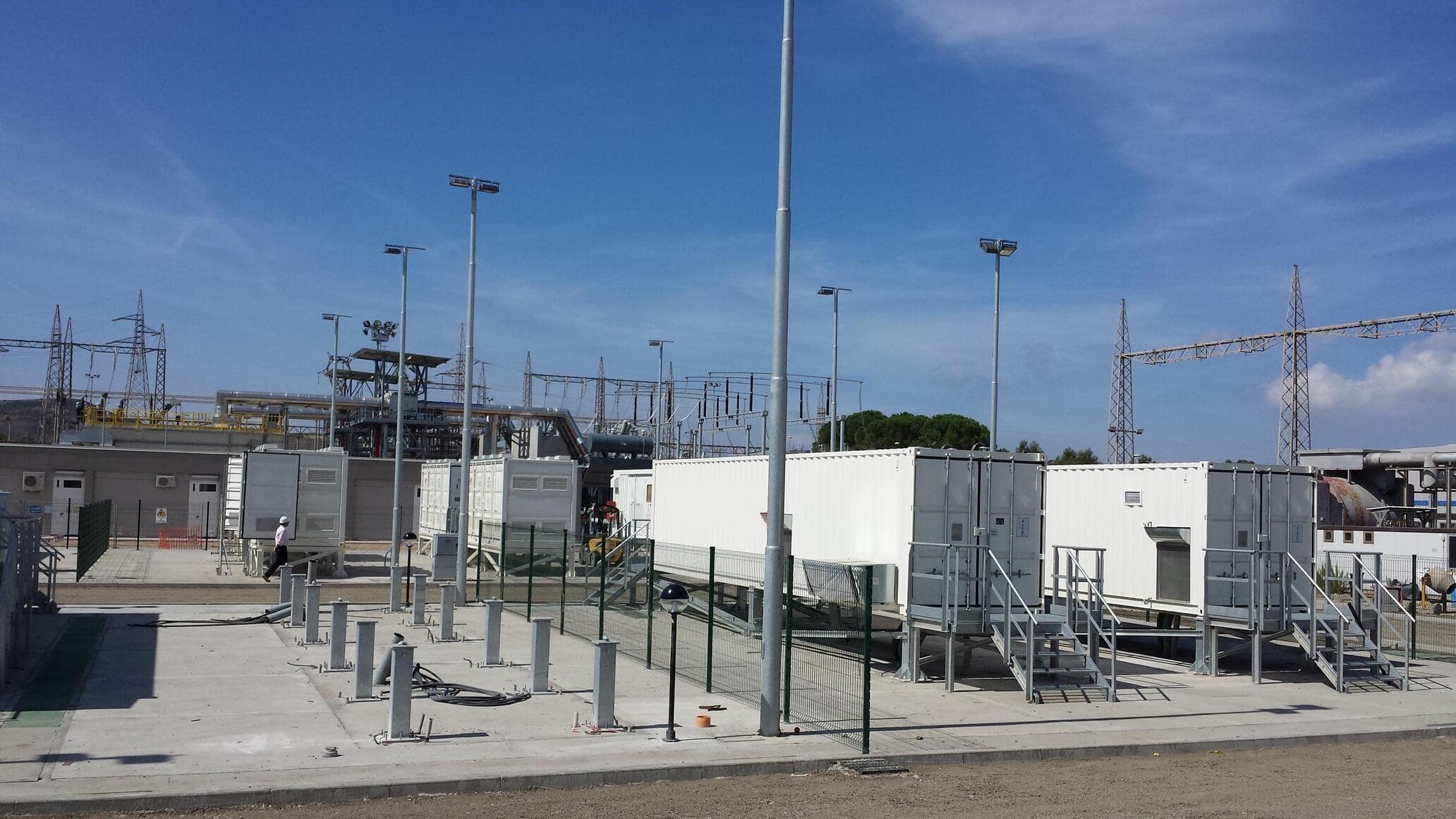
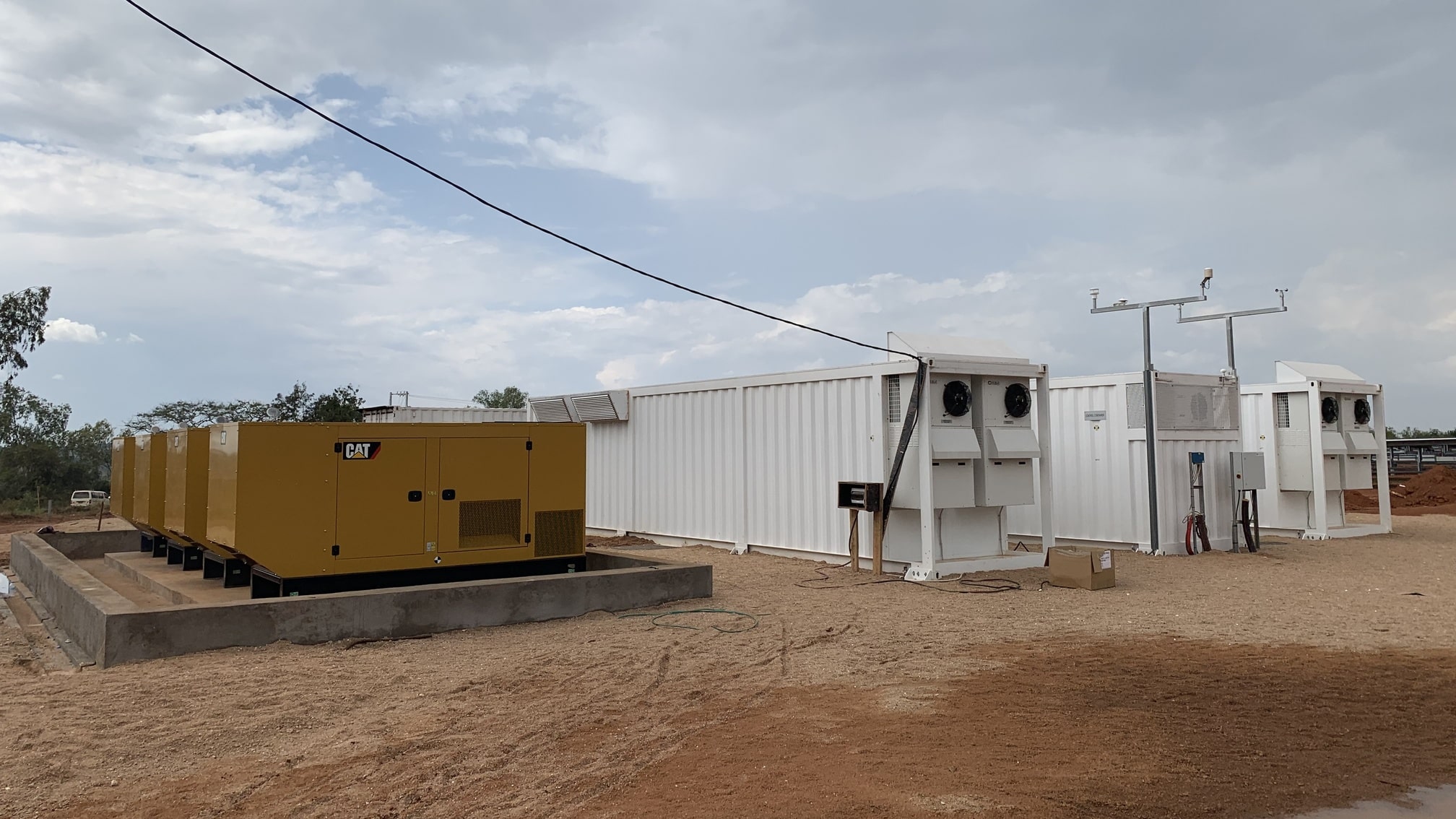
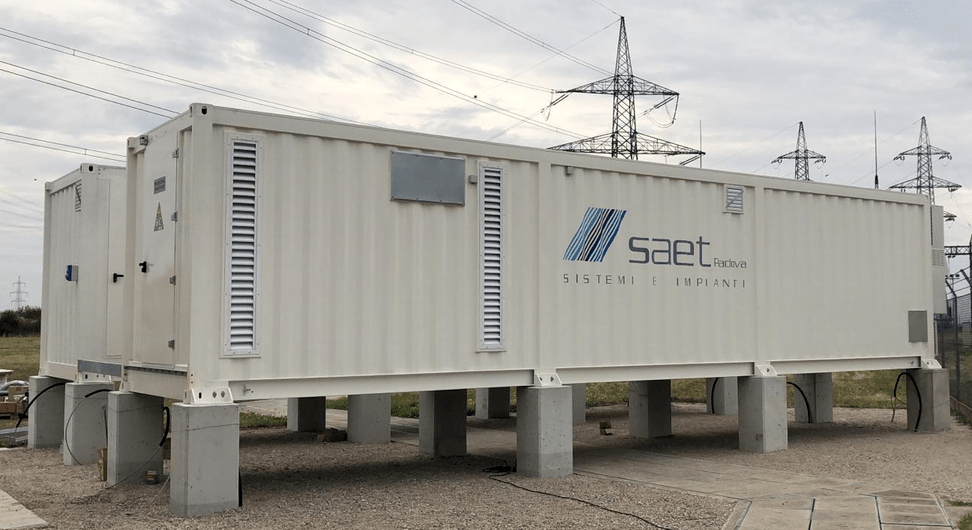
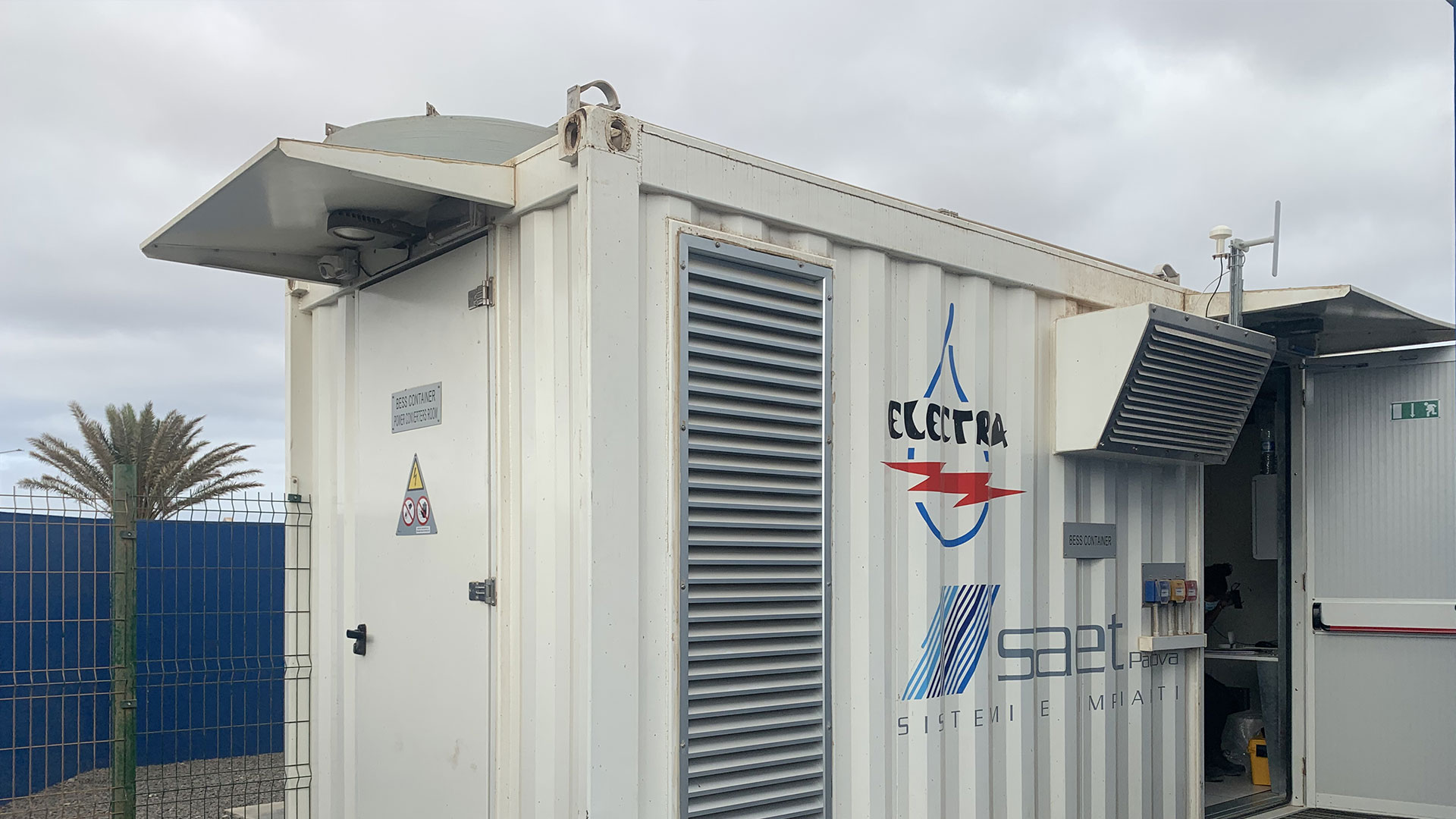
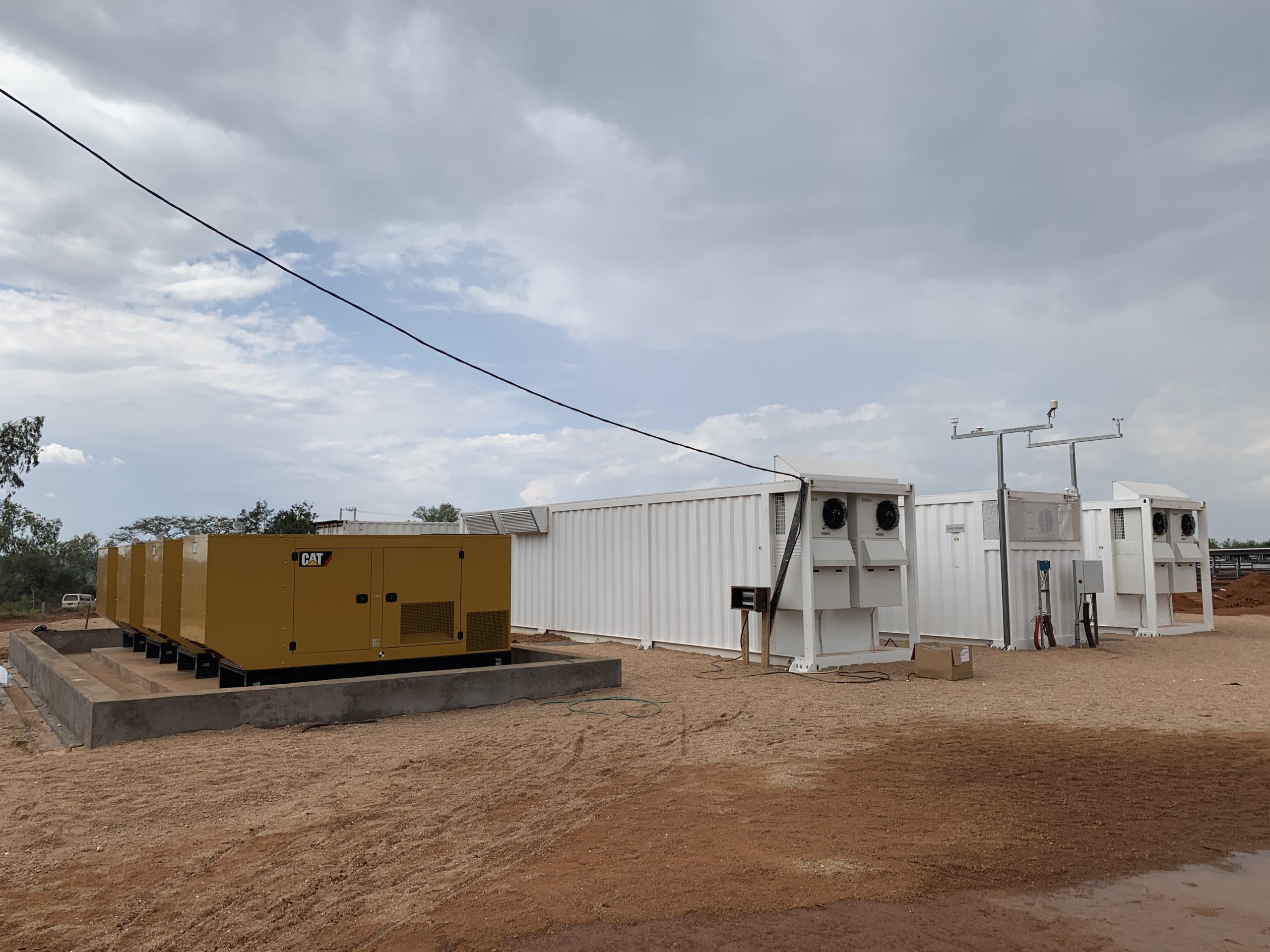
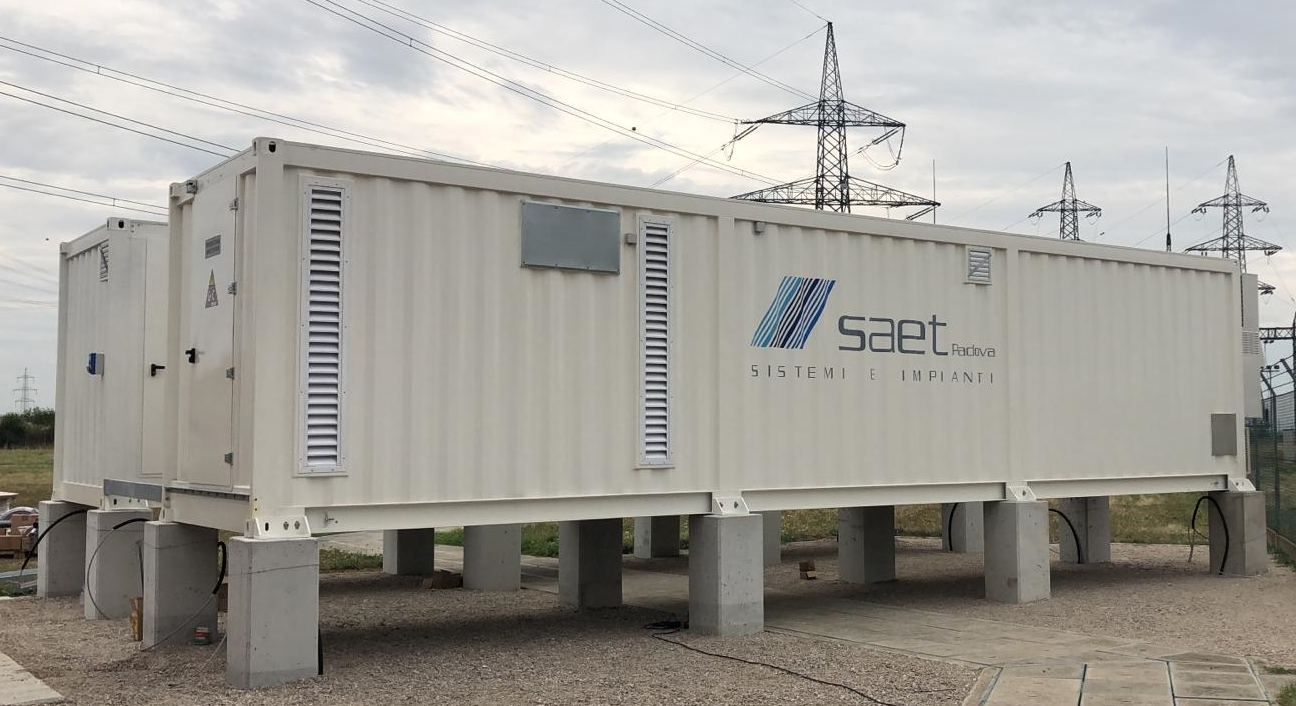
SAET has been a pioneer in the provision of energy storage solutions. Thanks to its strong expertise in grid and electrical systems, it was selected as early as 2012 as a supplier in the first Italian experimentations with storage systems for the electricity grid by ENEL and TERNA. SAET presented itself as EPC Contractor for the supply of turnkey plants, or as a system integrator in collaboration with the leading battery manufacturers in the international field; in this way, the company has consolidated its know-how on different battery technologies (lithium, sodium, flux) and built significant contacts to be competitive on the market, offering flexible and reliable solutions to customers.
Through its subsequent experiences in a number of foreign countries, SAET has engaged with different network code requirements, working in close contact with the transmission and distribution system operators of each country.
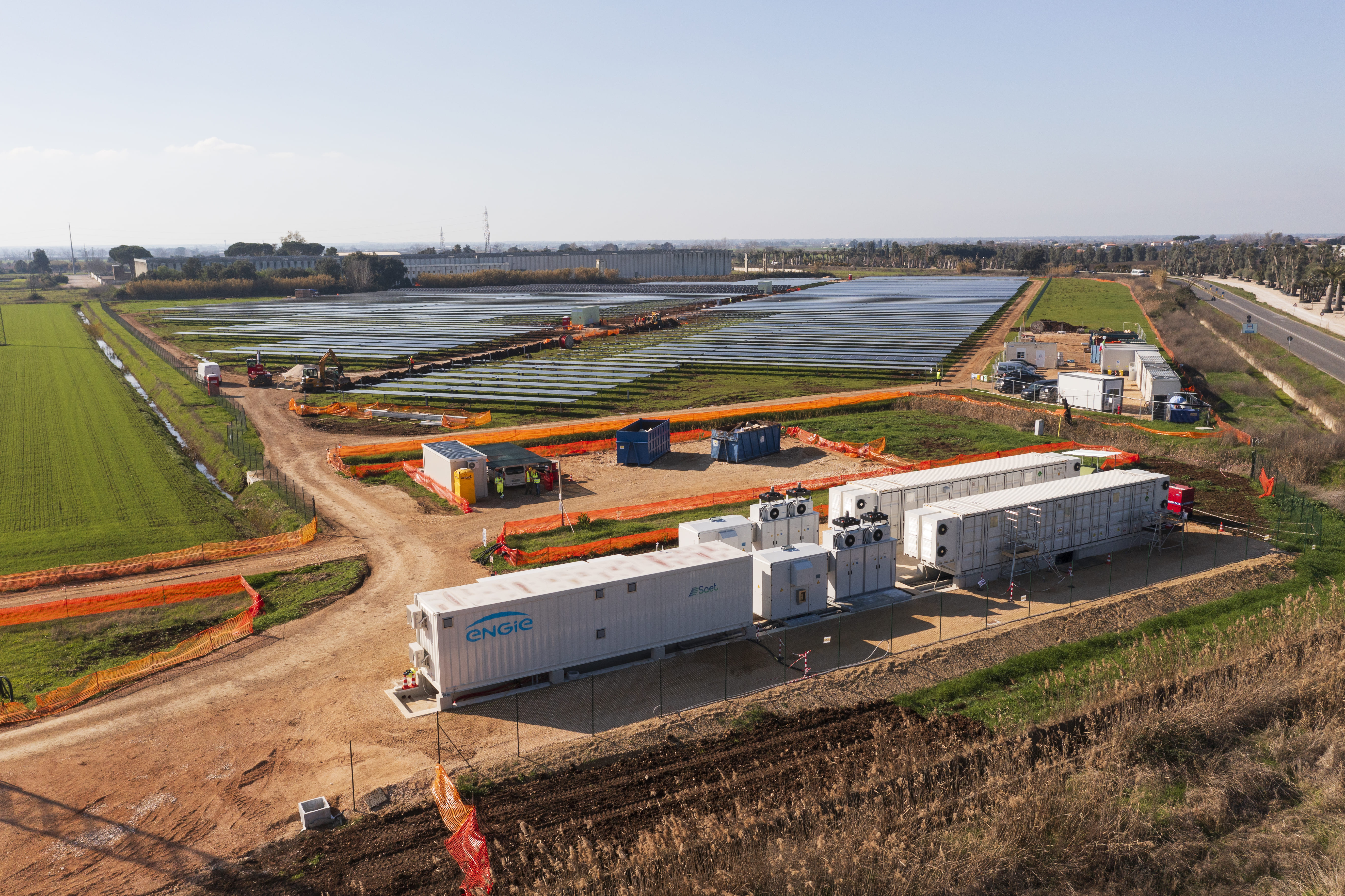
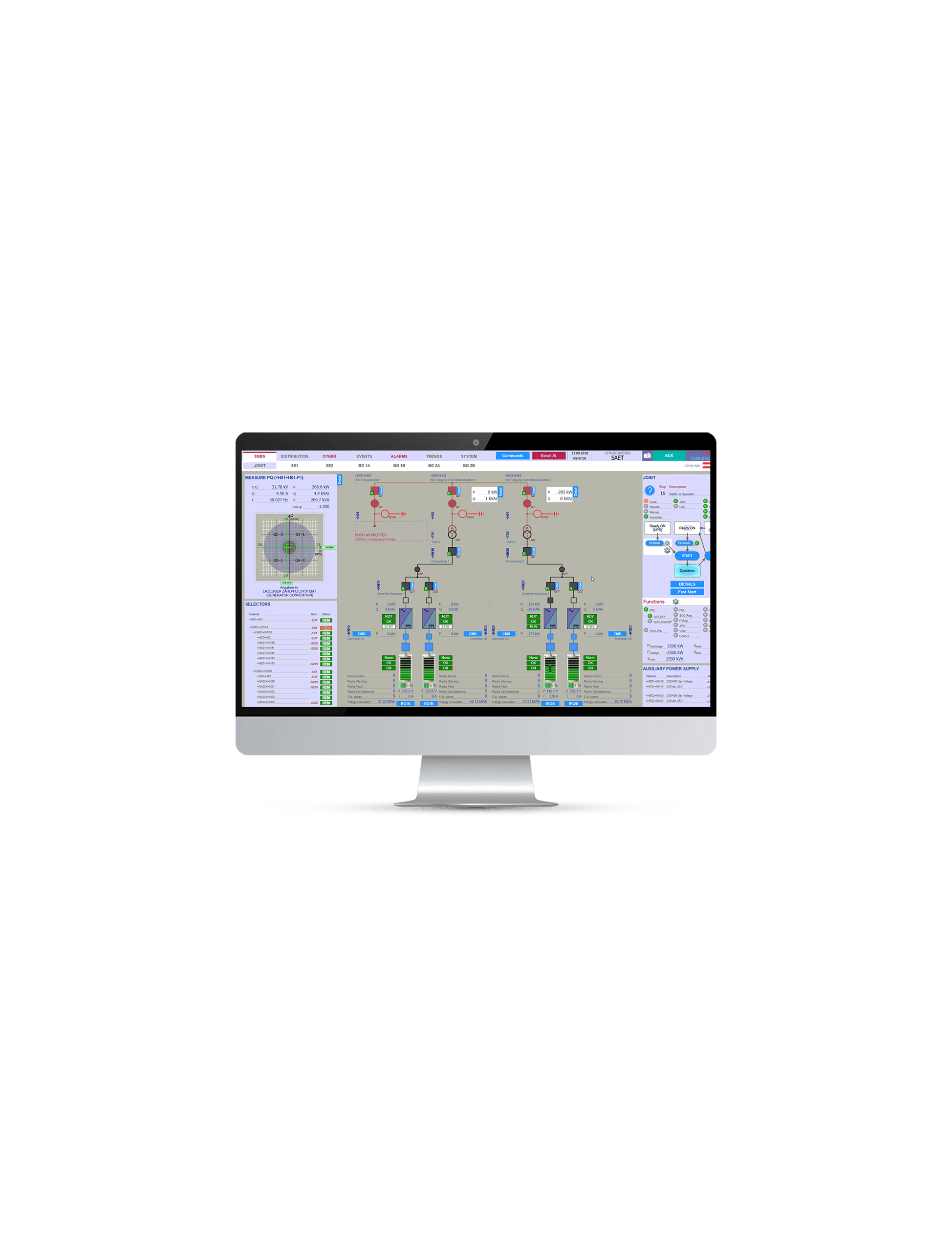
SAET is now present on the international Energy Storage market providing turnkey systems of various sizes, following the project from the initial steps (feasibility study and cost-benefit analysis), to the definition of the sizing and of the optimal energy/power ratio, up to the detailed design and optimisation of the storage system performance. This is followed by the procurement of components and their assembly, on-site installation of the system, and commissioning. The offer is completed by Operation & Maintenance services and remote control of the system.
In recent years, the increase in energy requirements has led to the realisation that the supply model based on fossil fuels is no longer sustainable, due to the environmental and climatic impacts of the greenhouse gases they produce. Driven by the scientific community and growing public awareness, practical agreements and policies to combat climate change have been drawn up at both global and European level for safe and sustainable energy centred on a strong increase in the share of renewable energy sources (RES) in the total energy mix. This strong increase in the share of RES in the electricity generation mix has, however, deep impacts on the electricity system. The latter is moving from a traditional, one-way structure to a more complex one with problems related to the characteristics typical of RES, i.e. a lower inertia and regulatory capacity, and non-programmability. These, combined with irregular location, can cause congestion and grid management problems. As a result, it is necessary to rethink the traditional electricity system and move towards the concept of intelligent network or smart grid, i.e. a network characterised by devices and procedures that can increase the security and reliability of the system and optimise the management of energy loads and flows.
In this context, a fundamental role is played by storage systems, which, thanks to their ability to store energy and return it at a later stage, are crucial for regulating the electricity system, increasing its flexibility. In particular, electrochemical storage systems have undergone significant technological development and diffusion in recent years, and have been installed at various points in the electricity grid to address a number of critical issues. Depending on the constituent chemical species, batteries are obtained with different technical characteristics and, in particular, different charge and discharge times, which adapt differently to the various grid services: power services (such as frequency and voltage regulation), characterised by fast charge and discharge times, and energy services (such as peak shaving and time shifting), denoted by longer regulation times.